A virtual private clouds (referred to as simply private cloud from here on) is a happy marriage between traditional enterprise IT and cloud computing. Unlike public cloud implementations, the hosted services in a private cloud are behind a corporate firewall. The enterprise has more control over its data and applications in this kind of setup.
For the past couple of years, private clouds have emerged as the hottest subcategory under cloud computing, as it expands the power of the cloud to new industries such as finance and healthcare, which have high levels of regulatory compliance requirements.
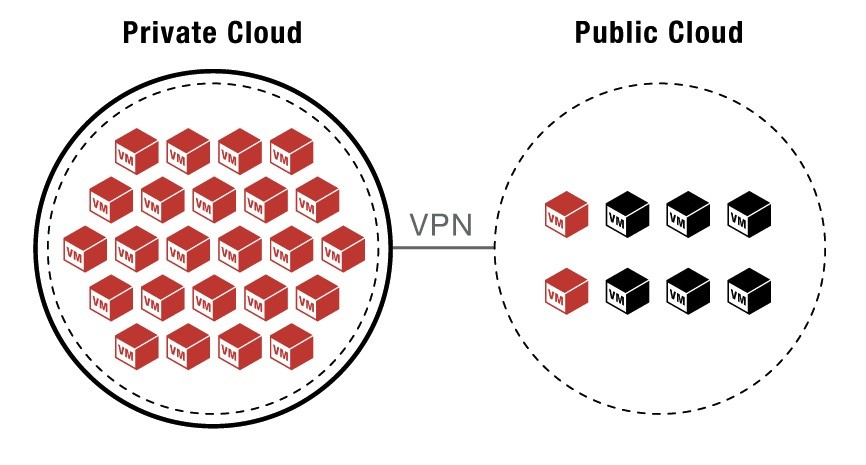
The disadvantages of a private cloud include higher initial investment, less flexibility and higher cost of maintenance compared to a public cloud. In a public cloud implementation you have very little CapEx (capital expenditure) and most of the spending is OpEx (operating expenses). This leads to a low-friction initial adoption. Private clouds are also more complicated to setup and more expensive to maintain than public clouds. Thus, these might not be suitable for smaller enterprises that don’t have a very high data security requirement.
Most of the major cloud vendors offer virtual private clouds alongside their public clouds. Amazon VPC, Rackspace Managed Private Clouds and Microsoft Managed Private Cloud are among the leaders, though this market is not surprisingly more scattered than the public cloud market.
By Balaji Viswanathan





