“Have you seen the price of Bitcoin?”, “You gotta get in on Ripple, it’s going through the roof!”, “Are we in a crypto bubble? Is it all going to crash?”
You may have heard all the hype about cryptocurrencies over the past year. But what people aren’t talking about as much is the valuable technology that underpins Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, and all the other cryptocurrencies out there.
That technology is blockchain, and it’s something that may have a tremendous impact on the future of your business, especially if international financial transactions, supply chain management, and data security are important to your company.
What exactly is blockchain, how can it help your business, and how can your business experiment with the technology?
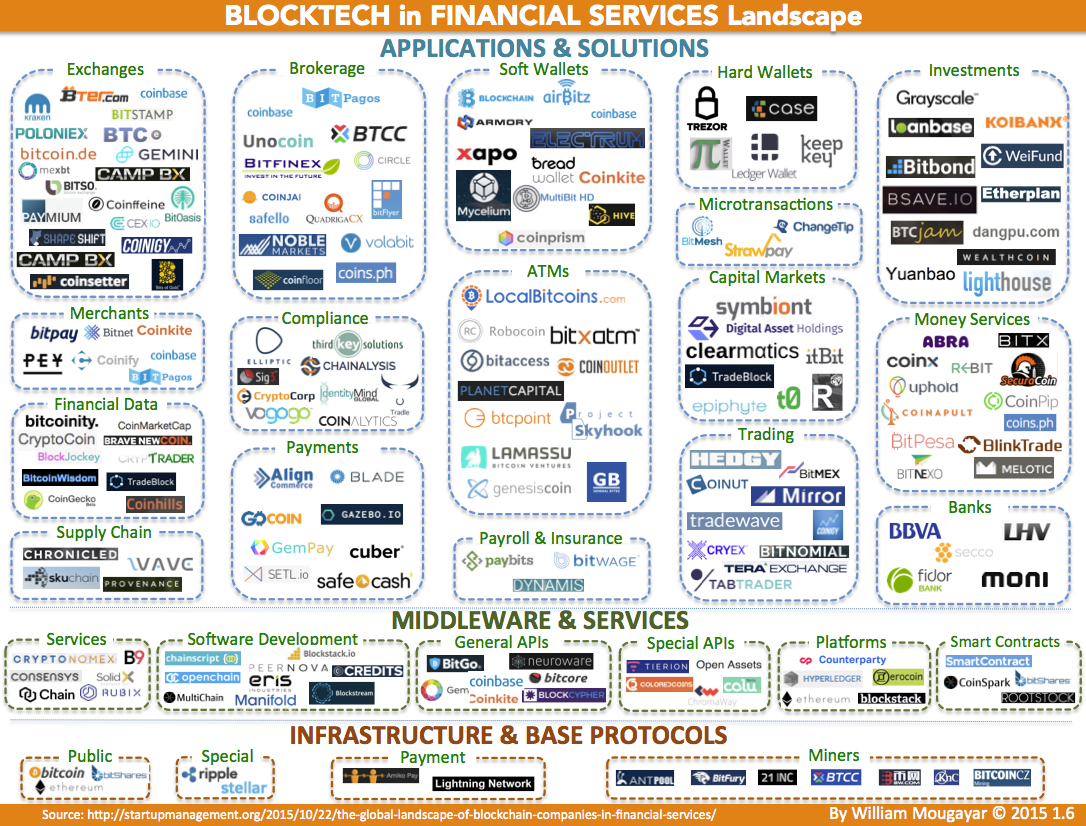
(Infographic Source: Startupmanagement.org)
The fundamental concept of a blockchain is that there is no centralized authority that lords over your transaction data and determines what is true or false or right or wrong.
When a transaction is requested, instead of a single, centralized party verifying and executing this transaction, it gets distributed across many nodes (aka other people’s computers), where it is validated and confirmed.
Once verified, a new block of data is recorded in hash functions and timestamps and added to the existing chain (hence, blockchain) of transactions, making your transaction immutable and permanent. Now, your transaction is complete.
The simplest example would be in the form of payments. Let’s say you want to pay your friend for tickets to Hamilton via PayPal. I know this is totally unrealistic because no one can get tickets to Hamilton, but let’s play along.
So, you go to your PayPal app and send her money. For this transaction to be verified and executed, PayPal, the centralized entity, must:
Now let’s say you wanted to pay your friend via Bitcoin. You make a Bitcoin payment request (usually through a cryptocurrency wallet like Coinbase) and the process would go something like this:
As you can see, this transaction isn’t verified by a single, centralized company like PayPal. Instead, it’s validated by many others who contribute to the blockchain in a way that is permanent and unchangeable.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Litecoin are mentioned as interchangeable with blockchain, but that’s only part of the story. Yes, these cryptocurrencies run on a blockchain, but there are many more uses of blockchain that can help businesses.
Most cryptocurrencies are overhyped, but in our opinion, blockchain is not. While it’s still in its early stages, there are many ways that blockchain can help businesses by providing better tracking capabilities and more reliable accountability measures.
With blockchain, transactions are executed without the involvement of a centralized third party, so in many situations they can can be processed much more quickly. Transactions can be completed within seconds or minutes, as opposed to days or even weeks if they were to go through an automated clearing house.
Additionally, transaction costs can be minimized when international payments are being made. Many banks charge large international transfer fees, which can be lowered or avoided using cryptocurrencies. Blockchain payments also don’t have to go through foreign exchanges, so you can steer clear of all the exchange rate fluctuations, potentially saving you lots of money.
For example, Australian car manufacturer Tomcar pays some of its overseas suppliers with Bitcoin and accepts the cryptocurrency from its customers through a partnership with CoinJar.
The company was paying 6-12% in transfer fees to its international suppliers, and now only pays about 1% per transaction. Because of its success with suppliers, the company decided to accept Bitcoin payments from its customers as well.
Supply chains can be huge beneficiaries of blockchain technology due to the traceability it provides.
Large companies’ supply chains are extremely complex networks of vendors located all over the world. Raw materials move across multiple modes of transportation, and it can be difficult to truly understand where product parts were produced and assembled. Hence, guaranteeing product quality and safety is tough.
Blockchain can help better track all this supply chain activity. Because each step of the supply chain can be immutably documented and this data can be accessed easily and instantly, companies can trace exactly where their products are sourced from, when each part was manufactured, and by whom.
Walmart has partnered with nine food providers and IBM to experiment with blockchain to trace sources of food. They’ve run pilots to track the paths of Chinese pork and Mexican mangos using Hyperledger Fabric, a blockchain framework originally created by IBM but now managed by the Linux Foundation. In the case that a foodborne illness occurs, Walmart can refer to the blockchain to easily pinpoint the culprit.
Similarly, Everledger has used blockchain to build a global registry for diamonds to stop the spread of conflict diamonds. They’re expanding their system to other precious goods like fine wine.
From Yahoo to Equifax, massive security breaches happen all too often.
While it isn’t a silver bullet to companies’ security woes, the distributed nature of blockchain is inherently more secure than its centralized database counterparts.
If a hacker or an evil insider gains access to a centralized database, that person can make edits to the data and use the stored information for nefarious purposes.
But because the data on a blockchain is distributed across the world, a single actor can’t make changes to the data without it being verified by the many others in the blockchain network. Thus, blockchain is especially useful for the security of very sensitive information such as financial, health, and identity data.
Blockchain is even being used to improve upon existing cybersecurity technologies, such as public and private key cryptography and storage of domain name service entries.
The Department of Defense’s Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is experimenting with blockchain to decentralize its back-office infrastructure to better protect its correspondence from exposure to hackers.
If national security can be secured by blockchain, imagine how it can help your secure your business’ data.
Blockchain remains a very nascent technology and still in the experimental phase for enterprises. While you can develop your own blockchain on top of technologies like Ethereum, this can take a lot of time and specific expertise that’s hard to come by because this technology is so new.
Hopefully you’re already benefiting from the use of a cloud computing platform. If so, a few of the major cloud Service Providers (hopefully one that you’re working with) are making it easier for you to deploy blockchains and experiment with how they can help your business.
As mentioned before, IBM created and supports the open-source Hyperledger effort with the Linux Foundation.
The core product is Hyperledger Fabric, which allows you to create core components like consensus mechanisms and membership services in a plug-and-play manner. There’s no cryptocurrency required to create a blockchain, transactions can be public or confidential, and smart contracts can be written in Golang or Java.
IBM also provides educational workshops, premium support, and even an accelerator to guide the development of new blockchain solutions.
The company has partnered with many customers across a variety of industries. In addition to the aforementioned partnership with Walmart and food manufacturers, IBM is engaging with various banks to build a blockchain-based trade platform, collaborating with Sony to develop a system to manage students’ learning data on the blockchain, and working with AIG on a multinational insurance policy powered by blockchain.
Microsoft launched its Blockchain-as-a-Service in 2015 in a partnership with ConsenSys, a company who builds decentralized applications on top of Ethereum.
The company developed a framework called Coco that makes blockchain networks enterprise-ready and is compatible with any blockchain protocol. Microsoft allows you to build different types of blockchains through its partnerships with various providers like R3’s Corda, Hyperledger, Quorum, and Chain. Its blockchain offerings also seamlessly integrate with its other cloud computing and software products.
Microsoft has scored contracts with Bank of America Merrill Lynch to speed up trade finance transactions, partners with EY and Maersk to build a marine insurance blockchain platform, and is pursuing the use of blockchain in the US Government with its launch of Azure Government Secret.
Oracle has worked hard to catch and keep up with cloud computing giants AWS and Microsoft. The company is betting that its blockchain offering, launched in October 2017, can help close the gap.
Blockchain represents a double-edged sword for Oracle, one of the largest database providers in the world. On one hand, the distributed nature of blockchain is diametrically opposite of the centralized nature of databases. On the other hand, Oracle databases are used by over 98% of the Fortune 500, so its blockchain offering has an organic entry point into all of these large companies and can extend the capabilities of their many ERP and database solutions.
Even though Oracle is a bit late to the game, when it sees a worthwhile opportunity, it goes after it hard. And Oracle definitely sees opportunity in blockchain.
The top cloud service provider isn’t completely committed to blockchain. At AWS re:Invent 2017, CEO Andy Jassy responded to questions about a blockchain offering by saying:
“We don’t build technology because we think it’s cool.”
But the company is investing in the technology through its partner ecosystem, with collaborations with Sawtooth, R3 Corda, PokitDok, Samsung Nexledger, Quorum, and more. And companies like T-Mobile and PWC have built blockchains with AWS at their cores.
It will be interesting to see if AWS fully jumps on the blockchain bandwagon like many of its competitors.
Blockchain can be the technology that may fundamentally change how the internet works. And there are many ways that your business can benefit from it, including transaction efficiency, transparency, and increased data security.
Cloud service providers like Microsoft, IBM, Oracle, and (maybe) AWS are building and improving upon tools that can help you experiment with blockchain and determine how it can help your company.
By Mike Chan