AWS serverless compute services allow to build and deploy applications on AWS cloud without having to manage the servers. AWS serverless platform enables vendors to deploy cloud solutions without server provisioning, deploying, maintaining and monitoring applications, databases or storage servers. It contains features like customized configuration, easy maintenance, strong security, scalability, high availability, monitoring etc.
Serverless does not mean to execute application without servers. It is a model followed by cloud providers, where provider manages machine and resources on their own infrastructure, and provides services via dynamic allocation of machines and resources to build and run applications and services, which is known as “BaaS” (Business as a service) or “FaaS” (Function as a service) where code is executed in ephemeral Containers. Pricing is based on resources consumed during execution of task.
Cloud Logic Layer
AWS Lambda can act as logic layer for all containerized and microservices applications
Orchestration Management
Coordinate and manage the state of each distributed component of serverless application using AWS Step functions
Application Lifecycle Management
Continuously deliver your serverless applications using lifecycle management tools such as AWS CodePipeline
Security and Access Control
Secure entire environment and AWS Resources with AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management) and Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
Reliability and Performance
AWS provides highly available, scalable and secure services at lower cost
Global Scale and Reach
AWS offers a broad set of global products. Mostly all serverless services are available in multiple AWS Regions
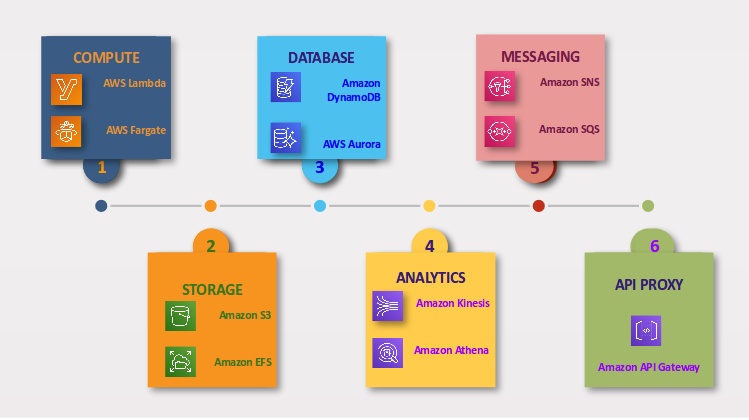
Fig 1 – AWS Serverless Services
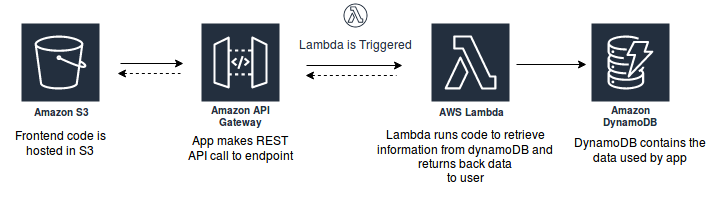
Web Applications
Build Serverless web applications that automatically scale up and down and run in highly available configuration across multiple available AWS Regions with zero infrastructure effort required for scalability using Amazon S3, Amazon API Gateway, AWS Lambda and Amazon DynamoDB.
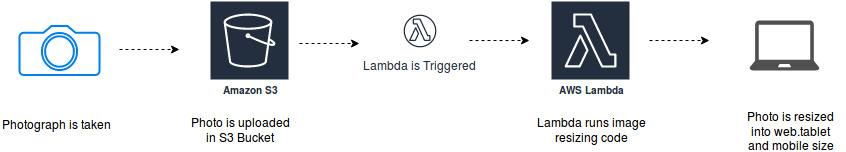
Real-time File Processing
After uploading the data in Amazon S3, S3 is able to trigger AWS Lambda to process the data instantaneously. AWS Lambda can be used to generate thumbnail images, transcode videos, index files, process logs, validate content, aggregate and filter data in real-time.
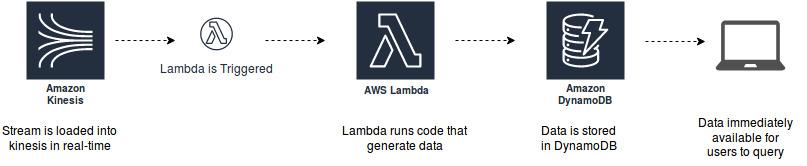
Real-Time Stream Processing
It is possible to process the real-time streaming data in AWS through AWS Kinesis and AWS Lambda. Streaming data sources could be application activity tracking, data cleansing, log filtering, indexing, social media analysis, transaction under processing and IoT device data telemetry and metering.
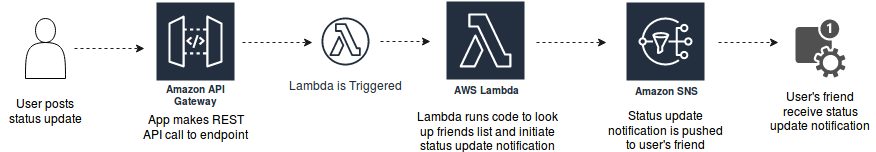
Mobile Backends
Build backend to authenticate and process API requests through AWS Lambda and Amazon API Gateway.
Serverless services make applications easier to scale and faster to develop without managing typical server-based infrastructure. Developers can focus more on core products instead of operating servers. As a result of which more and more organizations are preferring serverless platforms.
By Aarti Parikh