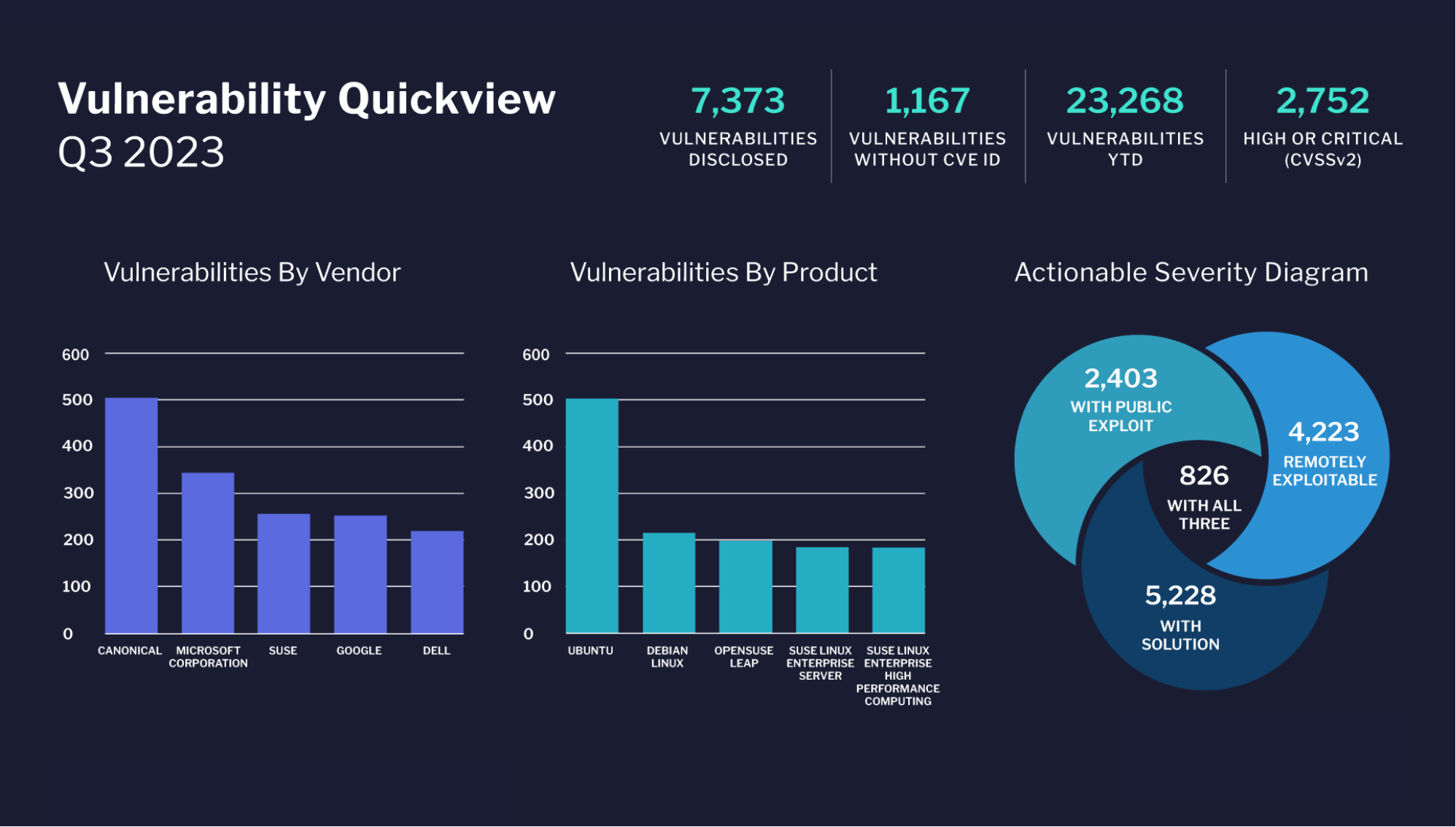
What Is A Database Management System (DBMS)?
(Updated: 04,22,2020)
A Database Management System, or DBMS, allows its users to create, read, delete and update data within a database. The management system works as an interface between users and/or application programs and the database to make sure that all data is well organized and easily accessible.
Within an organization, the DBMS manages three key aspects, the data, database schema and database engine and hence allows users to access modified and locked data. These three important aspects offer data security, concurrency, data integrity and all other uniform administrative procedures for remote DBA support.
Enjoy Logical and Physical Data Independence
A user can enjoy both logical and physical data independence through DBMS. It means the system can help users or applications by letting them know where all important data is stored. DBMS provides application programming interface for the database. There is no need to modify programs by developers since all the changes will be made by the DBMS.
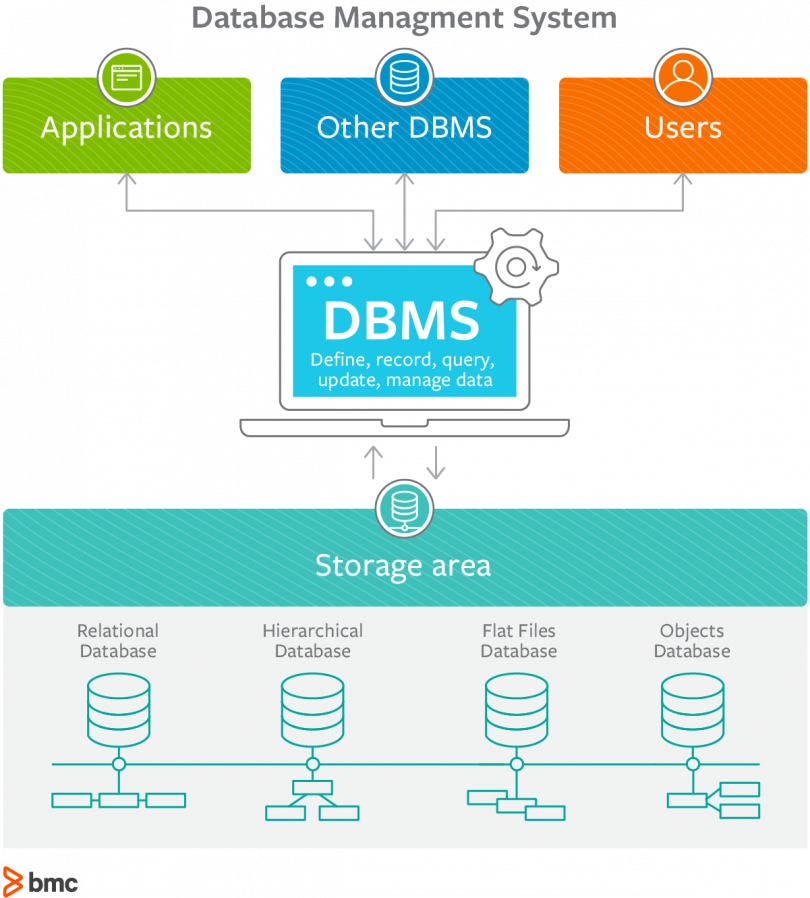
(Image source: BMC)
DBMSs have become popular in several industries and today more people are relying on these systems for their efficiency in improving data management within an organization. There are different types of DBMS available in the market, but all can be broadly classified as:
- Relational database management system – The product can be a bit expensive, but the system is adaptable for many cases.
- In-memory database management system – This system is being largely used by corporate sectors for its tremendous work efficiency, fast response times and overall better performance compared to other DBMSs.
- Columnar database management system – This system is well suited for all types of data warehouses comprised of a large number of the same kinds of data items.
- Cloud-based data management system – Here, the operators of cloud services will be responsible for maintaining the DBMS.
Advantages of Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Having a DBMS within an organization offers the following benefits for organizations:
- Control data redundancy – instead of having multiple copies of data for every application and/or user in an organization, DBMSs enable efficient usage of storage space by having centralized storage for all data.
- Uphold data integrity – this means that information stored in the database is always accurate and reflects the latest state of data. This is done by defining and enforcing data validation measures and other integrity constraints.
- Prevent data inconsistency – when applications have separate data, changes made on one set will not be reflected across other sets of the data within the enterprise, giving rise to inconsistency. DBMSs enable prevention of inconsistencies by eliminating data redundancy and also updating all occurring copies of the data with the latest modifications by different applications.
- Enable data sharing – new applications/users can be developed/ installed/added to the system without having to provide space for new data.
- Enable standards enforcement – with a centralized system, it’s easy to enforce any requirements/standards at enterprise, departmental, sectional and even national and international levels. Standards enable smooth transitions during changeovers and migrations.
- Enable access restriction – centralized data management through DBMS enables multiple user and application restrictions according to their data requirements. This limits unauthorized use of data and improves data security as well.
- Provide backup and recovery – DBMSs have robust systems to enable data recovery in case of failures and automatic backup for all organizational data according to predetermined schedules.
Cuts development and maintenance costs – unanticipated requests are easily addressed with DBMSs than conventional file storage systems. While the initial setup costs are large, costs of application development and system maintenance are much lower once the DBMS is in place.
- Enable concurrency control – a DBMS can allow multiple users to access and modify the same set of data at the same time, and reflect these changes in real-time. Another aspect is that the DBMS allows multiple views for a single database schema i.e. offering different interfaces for the same data according to user capabilities.
- Impose data models – DMBS can enable imposition of logical and structured organization of data to enable the organization to have a consistent data system in all its parts. It also provides for separation between physical and conceptual schema to offer a logical database structure.
- Enable easy modification – systems can be modified easily using DBMS to effect change in the organization. New data can be included without harming the existing data. Moreover, applications can be insulated based on how data is contrasted and stored in the DBMS.
Benefits of Remote DBA support
Organizations everywhere are looking for ways to cut down costs in order to stay competitive, this means that IT managers have more limited budgets within which to work, hence the need for more efficient solutions. Database administration is the most technical and vulnerable sector within the IT department, since it requires a high level of mastery and skill, which is hard to come by.
Majority of organizations have reached the conclusion that having remote database administration is the better, more affordable, option compared to training/recruiting in-house DBAs. The following are a few benefits offered by remote DBA management over in-house DBA.
- Expert support – rather than hiring inexperienced junior DBAs who are costly and may fail to deliver, remote services come with the advantage of experience in a number of fields hence will provide more effective and efficient management for the organization.
- High database availability – hiring expert services dramatically reduces incidences of downtime, such as would occur when the in-house DBA is unwell, leaves the company or is otherwise unavailable.
- Lower costs – perhaps the greatest advantage lies in the fact that remote DBA gives you the option to only pay for the actual services you require when they are required. This provides huge cost savings compared to paying a fixed high salary to a DBA throughout the year, including training costs to ensure they remain current.
- Good for smaller businesses – Properly trained DBAs are very expensive, meaning that young/small businesses cannot afford to have them on staff. Remote DBA services allow for scaled costing, which means that the business only pays for the services that they actually use. Service Providers have tailored packages for smaller businesses, which they can then scale upwards as the business grows.
- Providing business continuity – qualified DBAs are always in demand, which means that unless a company is ready to match every offer they receive, they will likely lose their DBA to better offers. Remote DBA offers you constant support and management for your database regardless of what’s happening with the service provider’s staff.
- Wide knowledge base – assuming the organization decides to change from one DBMS to another, the in-house DBA may not be conversant with the new system, costing the organization thousands of dollars and inefficient administration in the time it takes for the DBA to learn the new system. However, remote DBA service providers have on-staff skilled personnel with experience in all systems, meaning that your business won’t be affected should you decide to change to another DBMS.
By Jenny Richards