For the past few years everyone has marked-out a constant increase in public and private clouds. Whether to adopt a public cloud approach (off-premise IT capability or application, provided by others) or go for private cloud (on-premise enablement of cloud possibilities with existing IT) has always been an incensed topic for debate throughout the IT industry and the business.
Public Cloud: is a cloud computing infrastructure that can be easily assessed to the general public over the Internet. Public cloud services may be free or offered on a pay-per-usage model.
Private Cloud: is a cloud computing infrastructure that contains different and secure cloud based environment in which only required client can function.
For investment firms, cloud computing offers many advantages and allows the distribution of the resources in such a way that helps in simplifying infrastructure planning.
The immense difference between public and private cloud is that, in private cloud you are directly responsible for managing the machines and operating the entire infrastructure along with the billing of the services and payments of the machines. With public cloud you don’t have direct control to the machines or access to them.
Storing your data in the cloud signifies the exchange of your physical security for data security. For example, if you lose your laptop even than your data is still secured in the cloud. Some feels that public cloud is much more reliable than a private cloud. A private cloud favor all kind of IT fixes, updates and upgrade. It even allows IT to control the perimeters. Whereas on the other hand, a public cloud protect data by managing security on both software and physical level. Greater number of U.S Government has shifted to the public cloud including the banking industry.
But from an enterprise point of view, there are more security benefits to a private cloud as your information lives behind your firewall. Its fully owned infrastructure reduces security concerns and ability to satisfy regulatory requirements without requiring cooperation of cloud provider.
For every IT Executive cost management has always been a basic concern. Public clouds are cheaper when compared to private cloud. In public cloud no capital expenditures are involved as you don’t have to buy physical hardware as the server used are virtual and hosted by third party. Whereas in general, the private cloud are more expensive as enterprises storage and computing needs can play a large role. To put up private cloud service, an organization needs to capitalize in hardware.
Control:
In public cloud third party providers are main supervisors of data systems. So many organizations believe that they don’t have ample charge over their personal data. Whereas in private cloud, hardware is on-site thus organizations has direct control over the data system.
Internal IT employees are not in charge for maintaining the system, as public cloud services is hosted off site. As everything is managed at host company thus allow user to update or introduce technologies into the system, so public cloud requires no extra maintenance. But private cloud needs on-site maintenance as it is hosted at the company’s site therefore organization are responsible for supplying sufficient power, cooling and other general protections.
For Instance, if a company handle more than one data center with private cloud, the on-site maintenance increases extensively.
Many organizations prefer public cloud solution for its on-demand capacity and virtually unlimited scalability. Since the resources are offered on demand thus freeing an organization to choose the services and solutions depending upon business goals instead of considering IT conditions. However in private cloud Scaling might be less flexible as it entirely depends upon software solution that are being used and deployment architecture.
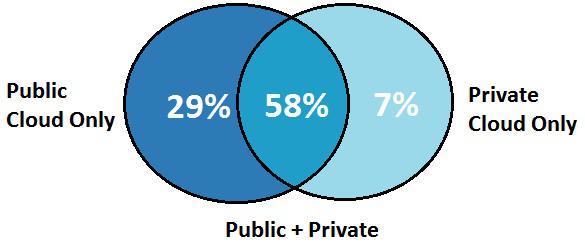
From above graphical representation it is quite clear that 94% of the Respondents are using cloud and running their applications or experimenting with infrastructure-as-a-service. It is also clear that 87% of the organizations are making use of the public cloud whereas 65% of the organizations are using private cloud. Public cloud being most widely applicable in delivering most value to a majority of business. The private cloud, on the other hand, is inefficient and encourages bad overprovisioning.
With cloud computing technology, huge pools of resources can be easily connected via private or public network in order to achieve and deliver dynamically scalable infrastructures for application, data and file storage. Moreover, application hosting, content storage, costs of computing and delivery can be significantly reduced.
By Sudhi Seshachala





